The control surfaces, including the rudders, were embedded in the wing itself. The inverted gull wing design is one of the most striking and interesting wing designs. The basic characteristics of modern subsonic wings—including those of all the airplanes of World War II—appeared early in aviation history. The wood wing of the Fokker D.VIII of 1918 was of moderate taper, with an aspect ratio of six, a relatively thick airfoil section, recessed ailerons, and a cantilever structure free of external bracing.
Follow NASA
You can refer to the image earlier in this post where the formulation of the equation to calculate Aspect Ratio is shown. The few examples given above illustrate just how useful a parameter wing loading can be; especially when just starting out on a new aircraft design. Of course sizing a wing in this manner is very crude and should only be used as a starting point in your wing design. You will need to take into account the mission (set of requirements) the aircraft is designed around and build your wing with a view to accomplish this mission.
Wing Structural Components
However, this is more than compensated for by the fact that this configuration is very well balanced. This design means that mid-wing aircraft have a large control surface area. The inverted gull arrangement was a favorite of Richard Vogt, the highly creative chief designer of the German firm of Blohm & Voss. He used it in a dive bomber that resembled a baby Stuka, and in the Ha 139, a four-engine floatplane that flew passenger- and mail-service routes over the South Atlantic before the war. Vogt then tried the opposite arrangement—the upright gull wing—on a three-engine flying boat. What made the game of airplane design difficult and seductive was that links between causes and effects were often obscure.

Northrop’s Charge
The rounded wingtip survived as a relic of the ideal ellipse until North American’s P-51 and Grumman’s F6F Hellcat abandoned even it. The Hellcat continued the practice of rounding empennage tips; not so the P-51, whose fin and stabilizer were squared-off as brutally as its wings. The same system could be used to make other structures as well, Jenett says, including the wing-like blades of wind turbines, where the ability to do on-site assembly could avoid the problems of transporting ever-longer blades. Similar assemblies are being developed to build space structures, and could eventually be useful for bridges and other high performance structures. The various structural design methodologies were discussed in part one of this series. This discussion on the structural design of a wing only considers the semi-monocoque design philosophy as it is the most popular structural layout in use today.
Elliptical Wing
After takeoff, the crew observed a "flight deck indication related to the right wing emergency exit slide, as well as a non-routine sound from near the right wing," Delta said in a statement. If we stay on this course with today’s aircraft, we’ll emit more CO2 than Germany, UK and South Korea combined by 2040. News from Dezeen Events Guide, a listings guide covering the leading design-related events taking place around the world. This project exists on a 55-acre property in the remote hills of Malibu with unique topography and panoramic views looking out to a nearby mountain range, a valley, and the Pacific Ocean with islands in the distance.
New JetZero Aircraft Design Will Make Flying More Sustainable - Tomorrow's World Today
New JetZero Aircraft Design Will Make Flying More Sustainable.
Posted: Sat, 02 Sep 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Search results:
“We hope that our approach improves performance, and thus saves resources, for a variety of future transport modes,” explains graduate student Benjamin Jenett. Because the overall configuration of the wing or other structure is built up from tiny subunits, it really doesn’t matter what the shape is. “You can make any geometry you want,” he says. “The fact that most aircraft are the same shape” — essentially a tube with wings — “is because of expense. It’s not always the most efficient shape.” But massive investments in design, tooling, and production processes make it easier to stay with long-established configurations. The problem facing aviation engineers was that, as an airplane approached the speed of sound, the air molecules around the wings created drag, forcing the plane to work harder to maintain its speed.
Preflight inspection is one of the most important steps you can take to ensure that your aircraft is fit for flight — and that includes inspection of your aircraft wings. Use this checklist as a guide in developing your own personalized system to inspect your wings before and after each and every flight. There are a number of different options that are available, such as digital paint support, textures, shaders, and many other features. This 3D software also has the ability to add ailerons, wings, landing gear, and various different nacelles to the plane. One of the best features of this aircraft design software is that it can work with both conventional and future type free CAD software, so it is able to meet a wide range of design requirements. Such software has to provide a long list of features that allow users to design a mechanically sound and reliable aircraft.
How a NASA Engineer Created the Modern Airplane Wing
An inconspicuous but important feature of every wing was its profile, or airfoil section. National centers for aeronautical research in France, Germany, England, and the United States had compiled families of airfoils adapted to airplanes of various speeds and wing loadings. Most of these airfoils had been created using abstract mathematical procedures that were not related to the physics of fluid flows, but simply yielded smooth shapes that happened to be rounded at one end and pointed at the other. The aerodynamic characteristics of those shapes were then measured by wind tunnel testing, and designers would pick out suitable ones from catalogs. Although very uncommon for an airplane, if a wing is twisted nose-up along its span by increasing the wing twist from root to tip, it is called washin.
Load Factor
In both cases it is clear that the location of the highest shear and bending is the wing root. The combinations and configurations of aircraft wings are endless, and what a wonderful thing that is. Every wing shape has its purpose and place in the sky, crafted with a unique design to meet whatever goals pilots have for their aircraft. The Dihedral wing configuration involves a wing that is angled upward from the horizontal of the wings or tailplane of a fixed-wing aircraft. To simplify this explanation, a dihedral wing looks like it is slightly tilted upward.
One broke in two when a landing gear collapsed in a high speed taxi run test in 1950 and was destroyed. Several aircraft industry executives were called to testify, including Northrop who said there had been no dishonest influence in award of the bomber contracts or the cancellation of other contracts. By then—and although its supporters were not ready to concede the point—the Flying Wing had been effectively eliminated as a bomber.
While Airbus has not yet announced a program to retrofit airplane wings with sharklets, increased use of efficient wing and engine design could mean fewer stops when flying cross country. Taper ratio and the sweepback, or rearward slant of a wing, are two other design ratios used in wing design. Tapering (decreasing the length of chord from the root to the tip of the wing), causes a decrease in drag (most effective at high speeds) and an increase in lift.
This tutorial focuses on the structural design of an aircraft wing and introduces the various control surfaces attached to the wing’s trailing edge. Today, many airplanes have wings with sweepback, as shown in the figure below, but many lower-performance airplanes will have no sweepback. The use of inverse wing taper is unusual, i.e., the chord increases toward the wing tip. However, it has been used to address the problem of adverse stall characteristics and a tendency to spin, a common issue in the first generation of jet aircraft with swept wings.
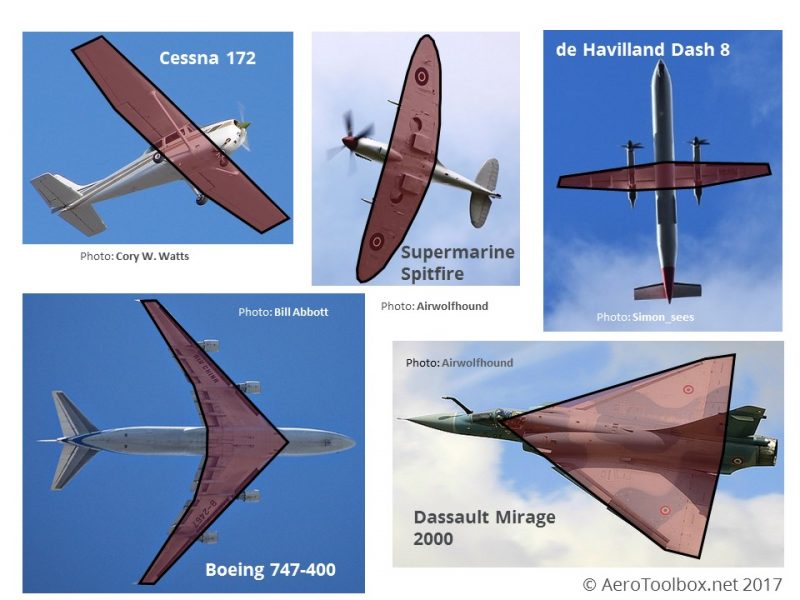
Wings are geometrically defined in terms of their span (distance from wing tip to wing tip), planform, twist (pitch angle) distribution, and cross-section (i.e., airfoil section shape or profile shape). The shape of a wing must be engineered to give good aerodynamic efficiency in lift production for the minimum amount of drag, i.e., the maximization of the lift-to-drag ratio, which is one fundamental goal in aerodynamic design. However, there will always be other aerodynamic requirements that will factor into the wing shape design, including its low-speed flight and stalling characteristics. Prominent characteristics of wings often look as though they must have some subtle or profound aerodynamic purpose when they really don’t. The planforms of wings from 1930 to 1945 show a great deal of variety, from straight leading edges and swept-forward trailing edges (de Havilland Mosquito) to the opposite (Douglas DC-3, North American T-6). The taste of designers, structural arrangements within the wing, and, occasionally, the need to adjust for an errant center-of-gravity location account for most decisions about sweep.
They support distributed loads and concentrated weights like the landing gear, engines, and fuselage. The front view of this wing shows that the left and right wing do not lie in the same plane but meet at an angle. The angle that the wing makes with the local horizontal is called the dihedral angle (if the tips are higher than the root) or the anhedral angle (if the tips are lower than the root). Dihedral is added to the wings for roll stability; a wing with some dihedral will naturally return to its original position if it encounters a slight roll displacement. You may have noticed that most large airliner wings are designed with dihedral. Highly maneuverable fighter planes, on the other hand usually have the wing tips lower than the roots giving the aircraft a high roll rate.

No comments:
Post a Comment